European Fruit and Wine Growers Hit by Devastating April Frost
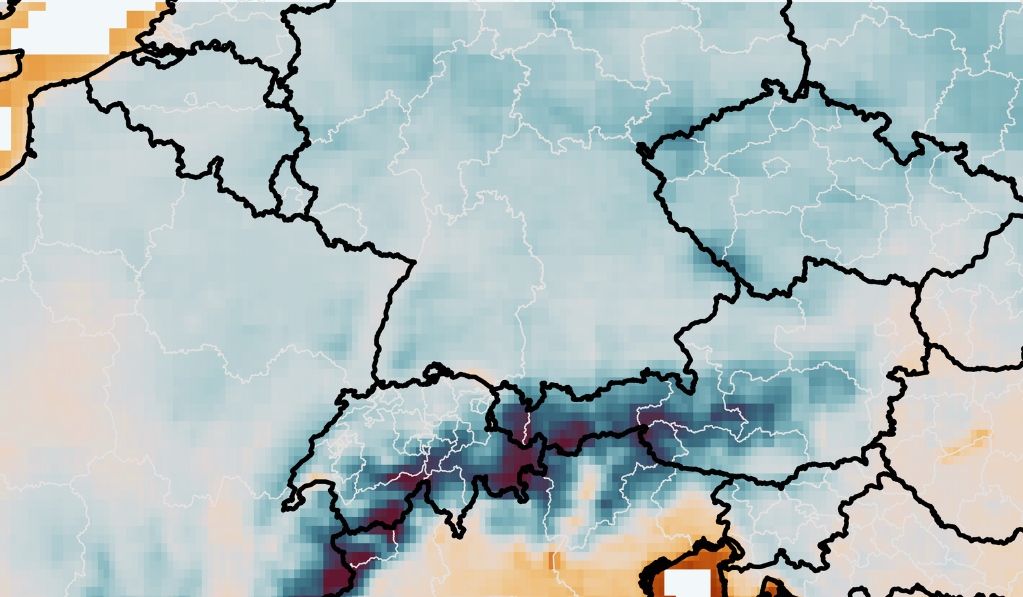
Below-zero temperatures in the second half of April 2024 have been devastating for European fruit and wine growers. Orchards and vineyards in the Czech Republic, Germany, Switzerland, Austria, Poland, Croatia, and Hungary have suffered severe losses. In the Czech Republic alone, the frost resulted in a loss of over 100,000 tons of fruit.
We use #TERRAClimateExplorer to compare the temperature anomalies between the 2024 and the 2017 spring frost, both of which occurred around the same time of year (second half of April). The daily minimum temperature anomaly for the 2024 event was relatively moderate compared to the 2017 event. In theory, this should have significantly reduced the extent of the losses. At the same time numerous crop insurance companies, particularly in Germany, assert that the 2024 frost was the most severe in decades.

How Growing Degree Days Shape Crop Vulnerability
Obviously, the severity of frost losses not only depends on the minimum temperature, but also on the phenological stage of the plant. Generally, a plant’s susceptibility to frost events increases as its phenology progresses.
Growing Degree Days (GDD) are a valuable concept in agriculture for measuring and predicting the growth and development stages of crops. The concept is based on the idea that plants require a certain amount of heat to grow, and this heat requirement can be quantified as a sum of the daily average temperature above a certain baseline temperature.
By applying a baseline temperature of 5°C, our analysis indicates that the vegetation’s developmental stage was significantly more advanced than usual at the start of the second half of April in both years. This suggests that the higher accumulated growing degree days (GDD) during this period likely expedited plant growth and development phases compared to the normal seasonal progress. As of April 16th, 2024, the accumulation of Growing Degree Days (GDD) has been significantly higher than normal, showing an advancement of approximately three weeks compared to the 30-year average. In other words, the vegetation in April 2024 has been more progressed than in any previous year. The extremely advanced phenology in 2024 has left the crops highly vulnerable to frost damage, even when minimum temperatures have only slightly dipped below 0°C.
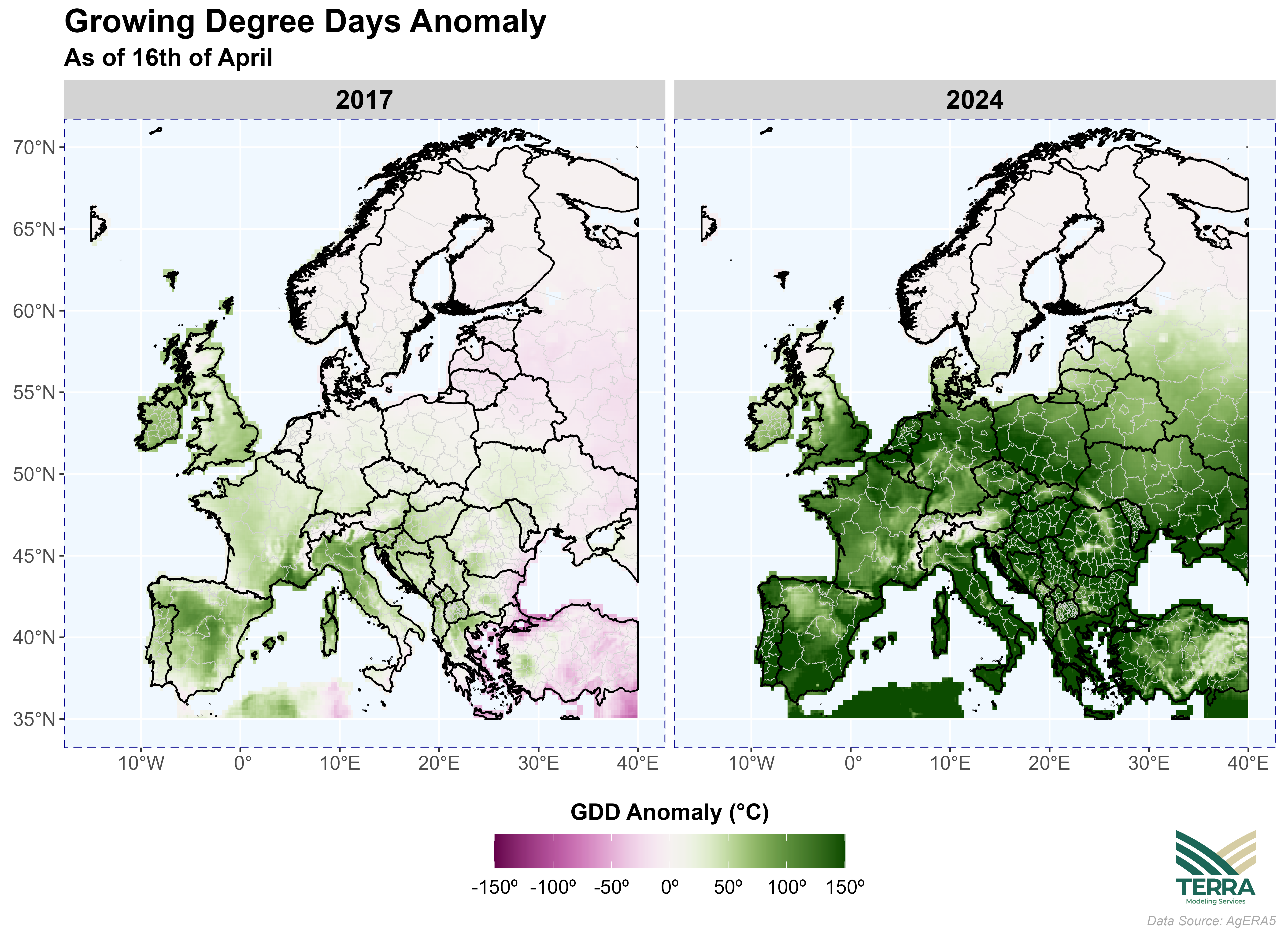
Figure 2: Growing Degree Days Anomaly as of 16th of April for 2017 and 2024.
Outlier or New Standard?
The extent of the positive GDD anomaly in 2024 is illustrated in Figure 3. Over the past 30 years, the GDD anomaly recorded as of April 16th, 2024, represents an unprecedented anomaly in the data set.

The question remains whether 2024 was just an outlier or if it has set a new norm going forward??
The #TERRAClimateExplorer
With the #TERRAClimateExplorer, accessing agro-meteorological insights has never been easier. The #TERRAClimateExplorer is a web-based solution that enables you to gather, monitor, and visualize historical and real-time weather and remote sensing data for any location worldwide.
Say goodbye to cumbersome processes and hello to streamlined efficiency. Experience the power of simplicity with the #TERRAClimateExplorer – where valuable weather data is just a few clicks away.
Contact us at info@terra-ms.com f you want to find out more, and subscribe to our newsletter to ensure you don’t miss any of our posts and articles.
#TERRAModelingServices